Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Wire mesh welding machines are essential tools in various industries, from construction to agriculture, and from industrial to residential applications. These machines create strong, durable welds that join wires together to form mesh patterns tailored to specific needs. The goal of this post is to provide the ultimate resource on using wire mesh welding machines for stronger, durable mesh. We will cover everything from understanding the machine’s components and the welding process to operating the machine, troubleshooting common issues, and considering post-welding factors. By the end of this post, you will be well-equipped to use a wire mesh welding machine with confidence and precision.
Understanding Wire Mesh Welding Machines
Wire mesh welding machines come in various types, each with its unique welding process. The three most common types are resistance welding, arc welding, and high-frequency welding. Resistance welding uses electrical current to generate heat, melting the wire and creating a weld. Arc welding employs an arc between two electrodes to melt the wire and form a weld. High-frequency welding uses high-frequency electrical current to heat and melt the wire, creating a strong weld.
Regardless of the type, wire mesh welding machines share common components. Feed rolls guide the wire into position, while welding electrodes apply pressure and heat to create the weld. Welding transformers control the amount of current flowing through the wire, and control systems monitor and adjust the welding parameters in real-time.
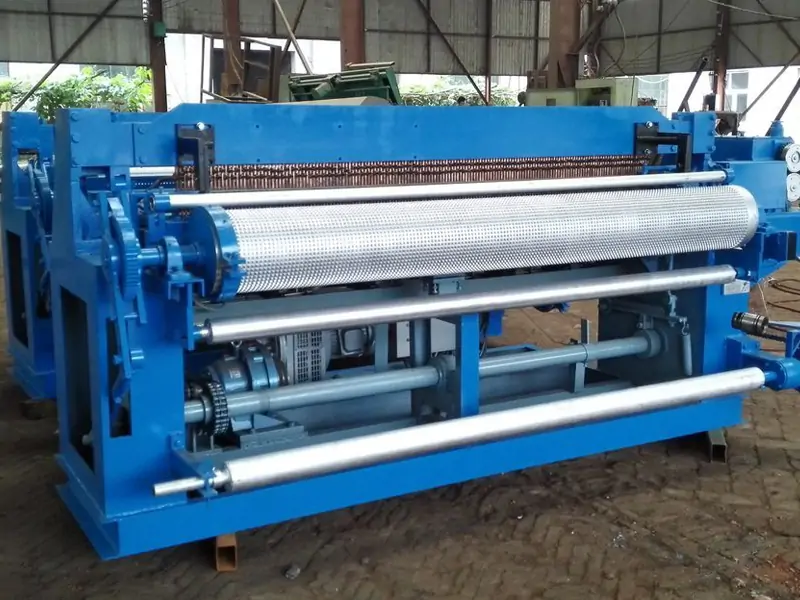

The welding process itself is crucial for creating strong, durable welds. The wire is fed into the machine, and the welding electrodes clamp down on it. Current flows through the wire, melting it and creating a weld. The electrodes then release the wire, and the process repeats, creating a continuous mesh pattern.
Wire mesh welding machines offer several benefits. They are highly efficient, capable of welding large quantities of wire quickly. They produce consistent welds, ensuring that each weld is as strong and durable as the last. And they are scalable, allowing for customization of mesh patterns and wire materials to suit specific needs.
Preparing for Welding
Before welding, it is essential to select the right wire material for your application. Various types of wire are available, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and others. The type of wire you choose will depend on factors such as strength, corrosion resistance, and cost. You will also need to consider the wire gauge and diameter, as these will affect the mesh pattern and overall strength of the welded mesh.
Designing the mesh pattern is another critical step in preparing for welding. The pattern you choose will determine the strength and durability of the mesh. Common mesh patterns include square, rectangular, and diamond shapes, but custom patterns are also possible. When designing a custom pattern, consider factors such as wire gauge, wire material, and the intended application of the mesh.
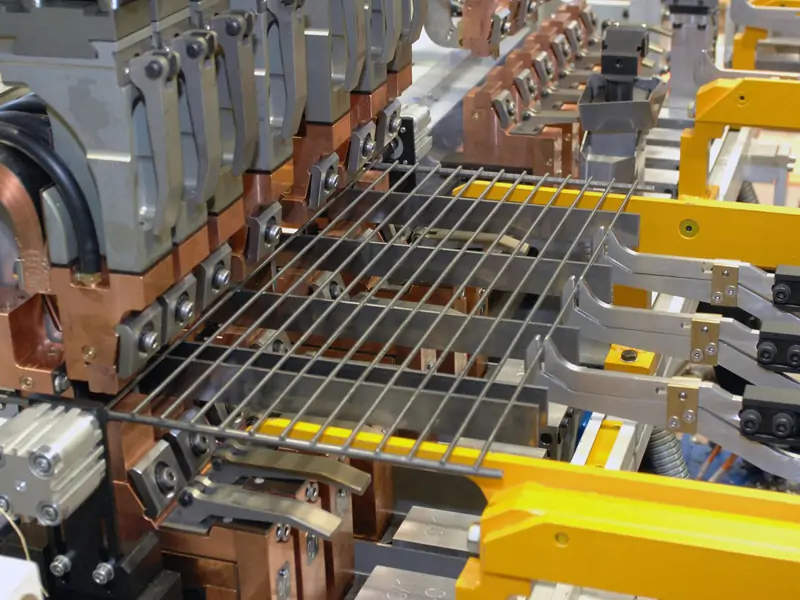

Once you have selected the wire material and designed the mesh pattern, it is time to set up the wire mesh welding machine. Adjust the feed rolls to guide the wire into position, and position the welding electrodes so that they clamp down on the wire at the correct point. Set the welding parameters, such as current, welding time, and electrode pressure, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations for your specific wire material and mesh pattern.
Operating the Wire Mesh Welding Machine
Operating a wire mesh welding machine is relatively straightforward once you have prepared the machine and set the welding parameters. Start by loading the wire into the feed rolls and initiating the welding process. The machine will automatically feed the wire into position, clamp down the welding electrodes, and create a weld. Once the weld is complete, the electrodes will release the wire, and the process will repeat, creating a continuous mesh pattern.
However, troubleshooting common issues may be necessary to ensure optimal welding performance. Problems such as poor weld quality, machine malfunctions, and safety hazards can occur. To troubleshoot these issues, refer to the machine’s manual for guidance on adjusting the welding parameters, maintaining the welding electrodes, and performing regular maintenance.
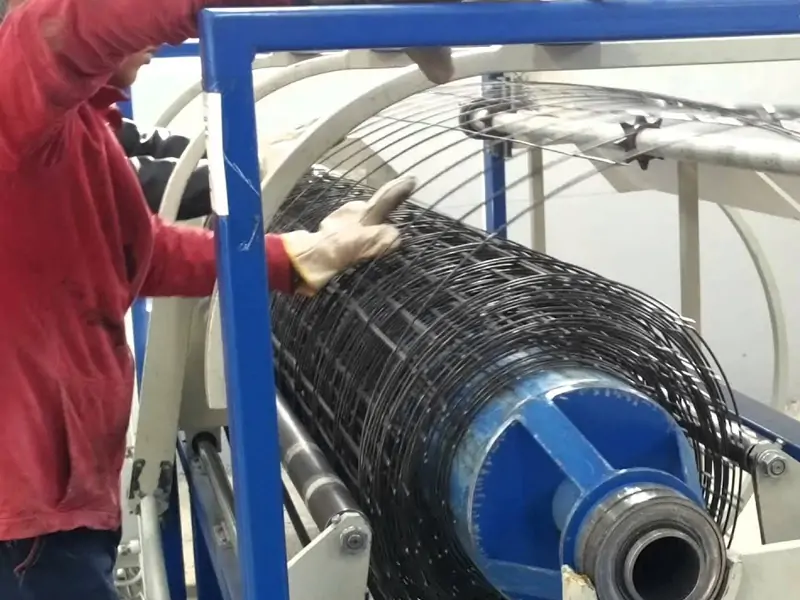

To optimize welding performance, follow these tips:
- Maintain the welding electrodes regularly by cleaning them and replacing them as needed.
- Keep the machine clean and free of debris to prevent malfunctions.
- Perform regular maintenance, such as lubricating moving parts and checking for worn components.
Post-Welding Considerations
Once the welding process is complete, it is essential to inspect the welded mesh for quality. Visual inspection can reveal flaws such as cracks, porosity, and incomplete welds. Destructive testing, such as tensile testing, can determine the strength of the welds. Non-destructive testing, such as ultrasonic testing, can detect internal defects without damaging the mesh.
After inspecting the mesh for quality, consider finishing options to enhance durability. Coatings, galvanizing, and other surface treatments can protect the mesh from corrosion and wear. When choosing a finishing option, consider factors such as the environment in which the mesh will be used and the desired lifespan of the mesh.

Proper storage and handling of welded wire mesh are also crucial for maintaining quality. Store the mesh in a dry, well-ventilated area to prevent rust and corrosion. Handle the mesh with care to avoid damaging the welds or causing the wires to become unwelded.
Applications of Welded Wire Mesh
Welded wire mesh has a wide range of applications in various industries. In construction, it is used for reinforcement in concrete, as well as for fencing and gabions. In agriculture, it is used for livestock fencing, animal enclosures, and greenhouse structures. In industrial applications, it is used for filtration, screening, and partitions. And in residential applications, it is used for landscaping, home security, and decorative purposes.
Case studies demonstrate the versatility of welded wire mesh. For example, one company used welded wire mesh to reinforce concrete walls in a high-rise building, significantly increasing their strength and durability. Another company used welded wire mesh to create custom enclosures for exotic animals, ensuring their safety and well-being.
If you have a unique application that requires a custom mesh solution, consider working with a wire mesh welding machine manufacturer. They can work with you to design and manufacture a custom mesh pattern tailored to your specific needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wire mesh welding machines are powerful tools for creating strong, durable mesh tailored to specific needs. By understanding the machine’s components and the welding process, preparing for welding by selecting the right wire material and designing the mesh pattern, operating the machine with precision and troubleshooting common issues, and considering post-welding factors such as quality inspection, finishing options, and storage and handling, you can achieve optimal welding performance and create high-quality welded wire mesh.
And if you find this post valuable, please consider linking to it as a resource on the topic of wire mesh welding machines.